ORDER BY Clause: You can use the ORDER BY clause in SQL to sort query results the way you want. Let me break it down for you.
ORDER BY Clause
Say you’re a college professor, and you need to print a list of your students in alphabetical order. You can do that easily with a simple query and the ORDER BY clause if you have the student data in a database. For more!
Here’s another example with a numerical column. Imagine you’re a sales manager, and you have a table called sales_performance in your company’s database. The table has columns like sales_person_id, name, territory, total_sales_value, and joining_date. You want to see a list of salespeople, ordered by their ID number from low to high.
— 1. This query is used to filter data based on alphabetical or number wise or accessiding or decending order (see 1st query).
— 2. We can always use arithmetic operators in the select clause and get the result as shown in 2nd query.
— 3. Note: The 2nd query is only applicable for MySQL, it might not work from database servers.
SQL Example 1:
SELECT *
FROM customers
ORDER BY state ASC, first_name DESC;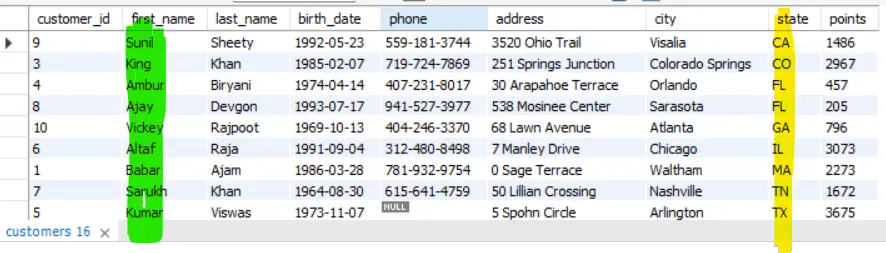
SQL Example 2:
SELECT first_name, last_name, 10 AS points
FROM customers
ORDER BY points, first_name;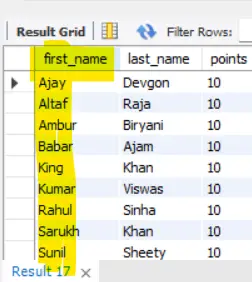
SQL Example 3:
SELECT *, quantity * unit_price AS total_price
FROM order_items
where order_id = '2'
ORDER BY total_price DESC;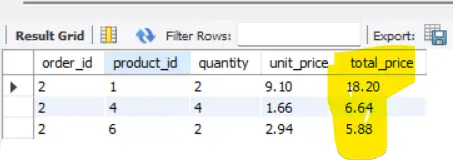
Watch Video!
Next Post >> #2.11) The LIMIT Clause
<<Previous Post #2.9) SQL IS NULL Operator
