SQL REGEXP Operator: The SQL REGEXP operator is a useful tool for finding complex string patterns in a database. It helps you get information based on specific patterns instead of simple character matches.
SQL REGEXP Operator
Sure! The SQL REGEXP operator is a useful tool for finding complex string patterns in a database. It helps you get information based on specific patterns instead of simple character matches. Here is a simple explanation:
What Is REGEXP?
- The REGEXP operator lets you test if a string matches a regular expression.
- A regular expression (or regex) is a special rule that defines or describes a search pattern or specific characters that an expression can contain.
- For example, you can create a regular expression to check if a string of numbers is a valid phone number. For more!
— 1. The name of the operator is Regular Expression (REGEXP) and it is similar to Like operator. But we have some advanced features in this expression.
— 2. If we specify “^” at staring of the string, then it says, “the last_name must start with field string” (refer 2nd query).
— 3. If we specify “%” at end of the string, then it says, “the last_name must end with field” (refer 3rd query).
— 4. We can use multiple pipelines to have multiple search patters (refer 4 query).
— 5. We can also use “[]” to specify rules. Suppose ‘[gvp]b’ then it will compare any value in 3 conditiond such as values starts from gb, vp and pb (refer 5th query).
— 6. We can specify ranges directly like [a-h]b, it check for all possibilities from ab, bb, cc, …..hb.
SQL Example 1:
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE last_name REGEXP 'vickey';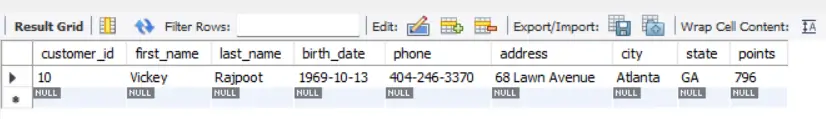
SQL Example 2:
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE last_name REGEXP '^raj';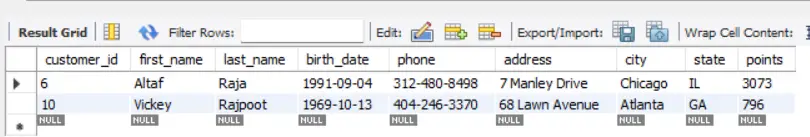
SQL Example 3:
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE last_name REGEXP 'ani$';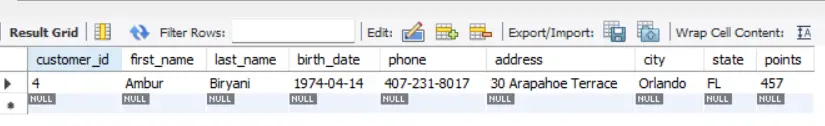
SQL Example 4:
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE last_name REGEXP 'raj|rajpoot|ani'; -- you can use "$" and "^" here as well!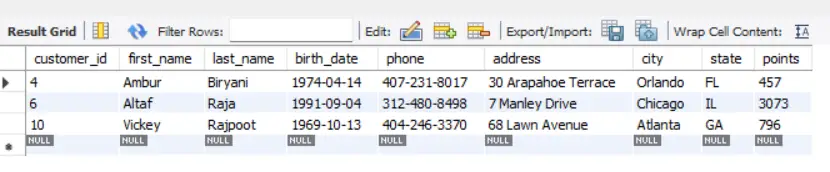
SQL Example 5:
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE last_name REGEXP '[a-z]e';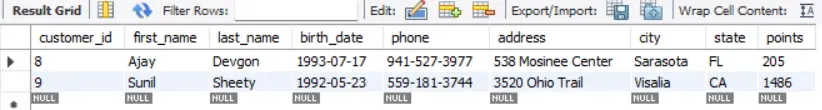
Points:
— // Using REGEXP for pattern matching in queries // —
— . (Dot): Matches any single character, except newline characters.
— + (Plus): Matches one or more of the preceding character or group.
— ? (Question mark): Matches zero or one of the preceding character or group.
— ^ (Caret): Matches the start of a string without consuming any characters.
— $ (Dollar): Matches the end of a string without consuming any characters.
Watch Video!
Next Post >> #2.9) SQL ISNULL Operator
<<Previous Post #2.7) LIKE Operators
